My Experimental Research
Development of Miniature Electron Propulsion System
In this experimental investigation, I focused on developing a compact Electron Propulsion Thruster optimized for air and water propulsion. The research aimed to create a miniature ionic propelled boat while maintaining a minimal form factor and achieving practical thrust generation.
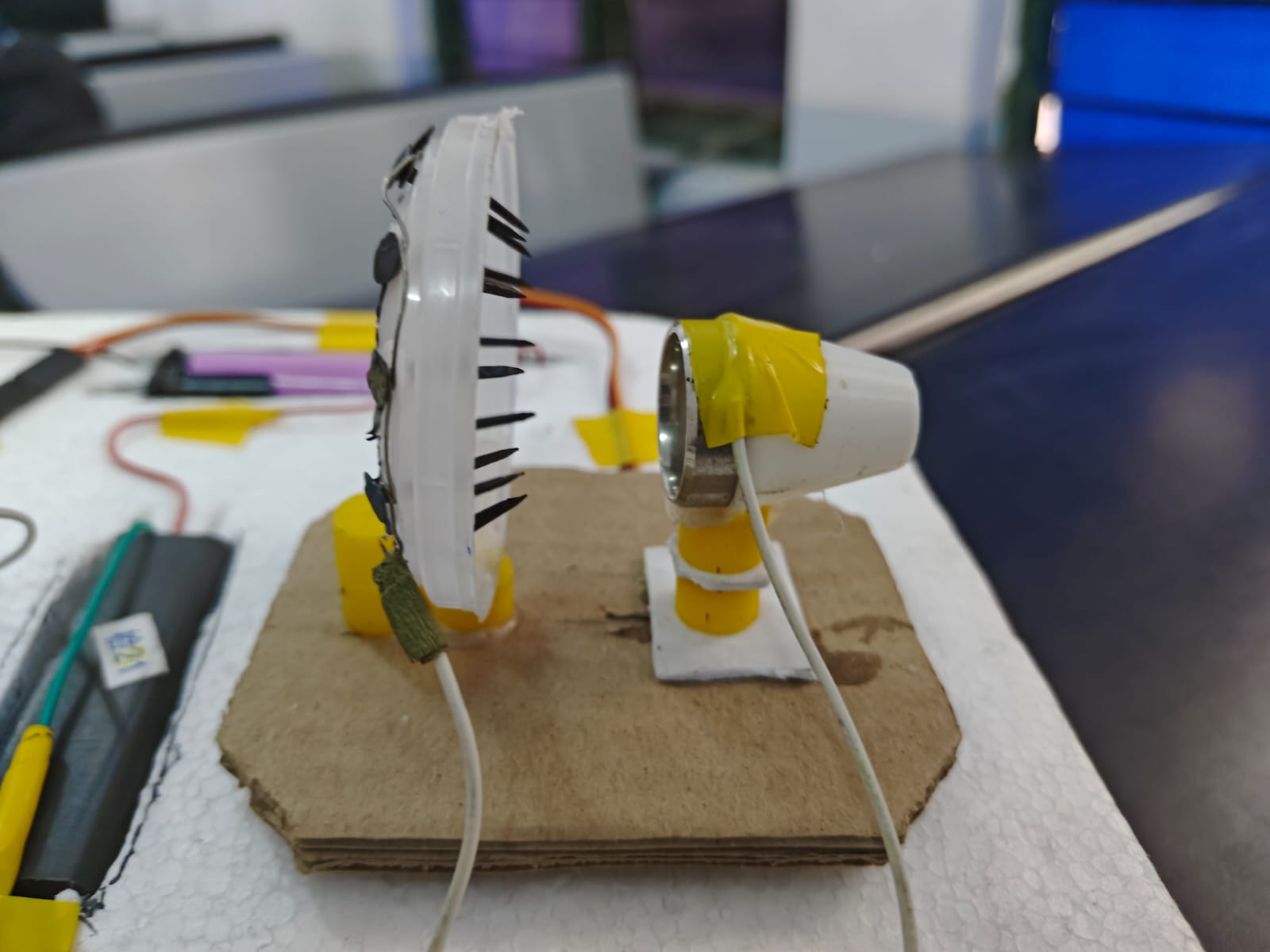

Side View - Ionic Propulsion Assembly
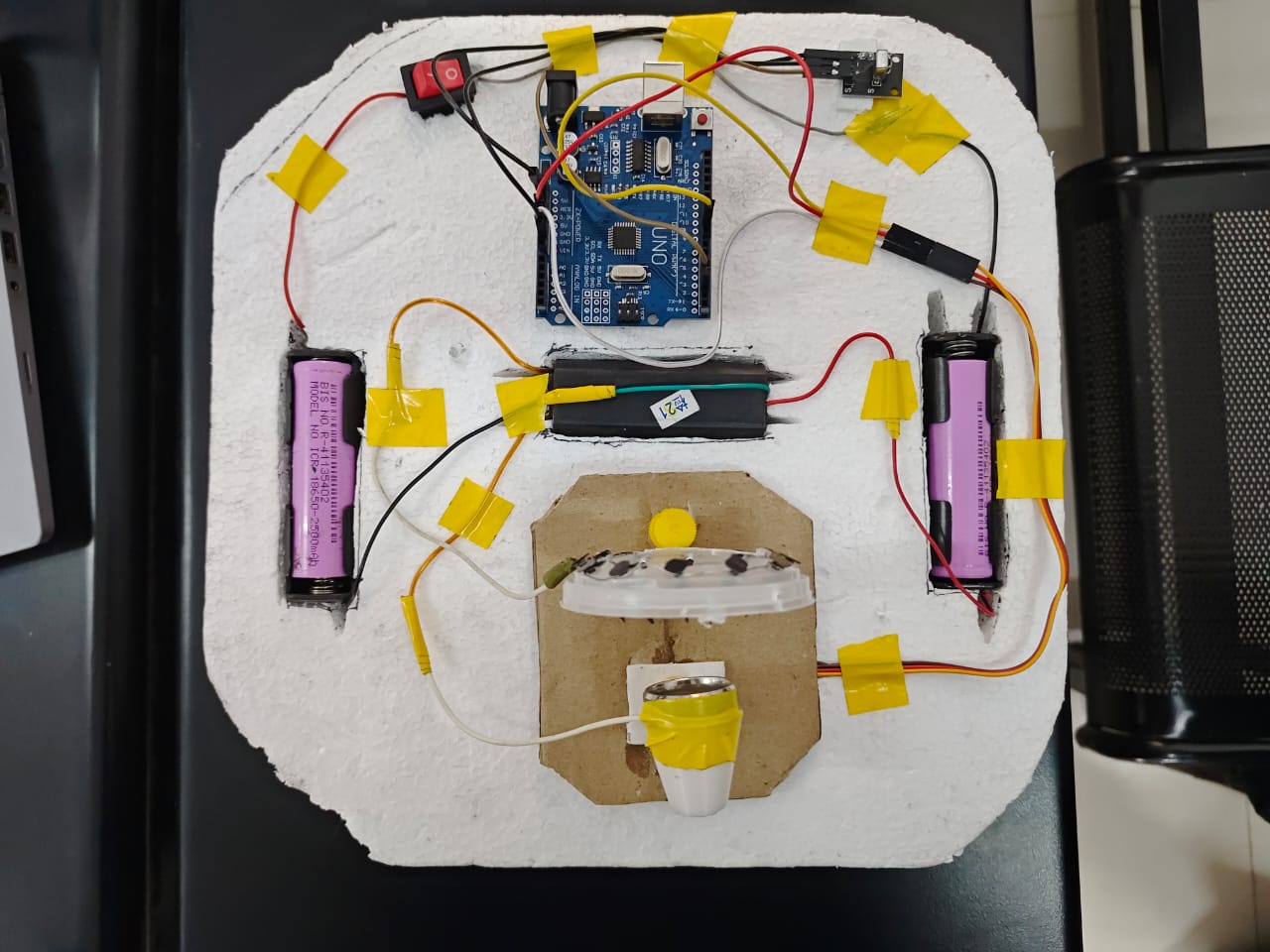
Top View - Boat Configuration
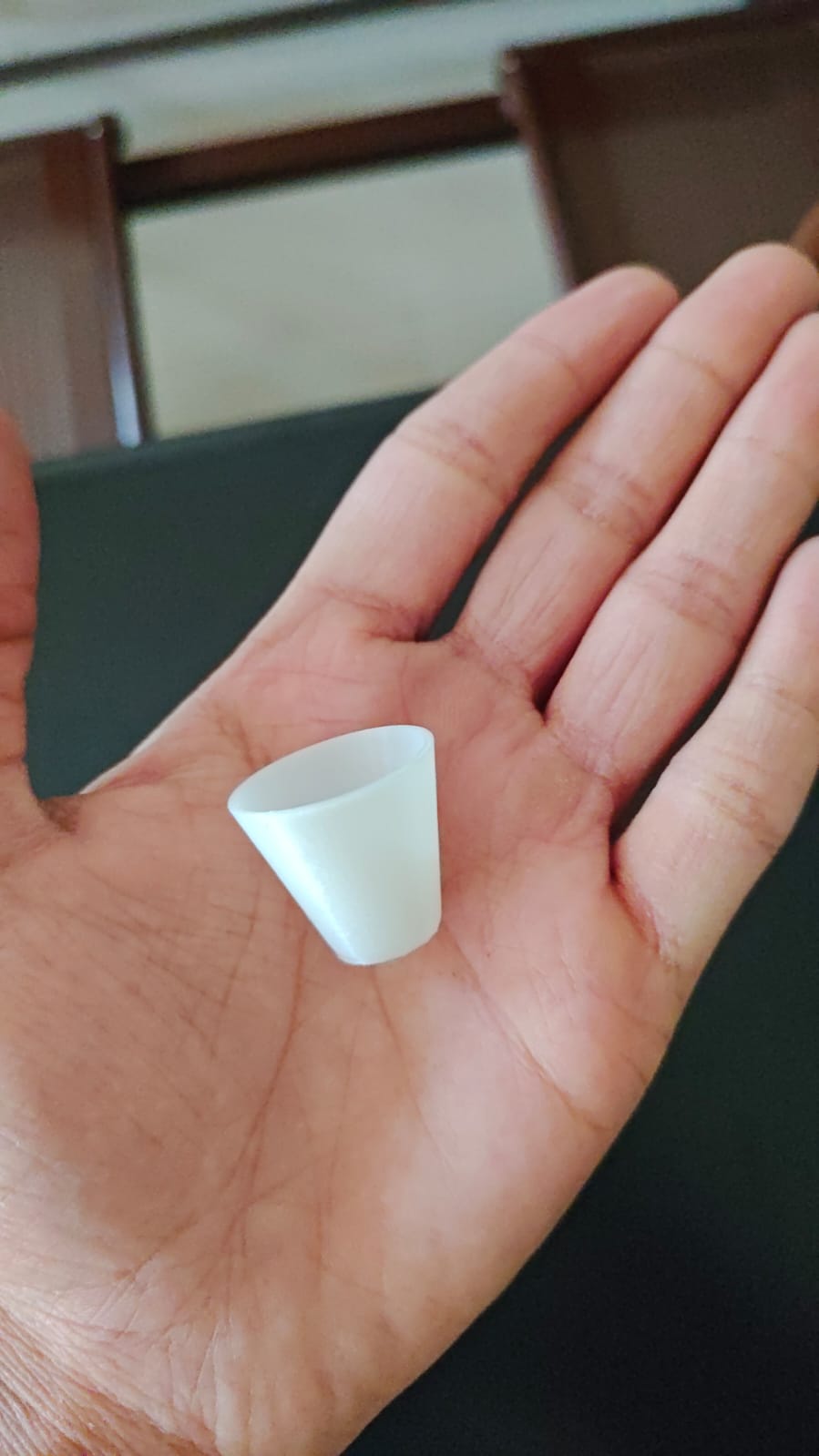

Custom Nozzle Design
Remote Control Interface Demo
Phone Control Interface Demo
Test Fire Sequence
Technical Specifications
- Voltage: 1 - 200kV DC
- Current Draw: 100-500μA
- Thrust: 5-10mN
- Operating Medium: Air
- Voltage depends on transformer/booster used
Design Features
- Custom electrode configuration
- Wireless control interface
- Integrated direction control
- Modular component design
- Compact form factor optimization
Achievements
- Successful electron movement
- Stable thrust production
- Remote operation capability
- Scalable design architecture
- Proof of concept validation